A Historical Look at Countries With Negative Population Growth
Unearth the accounts of nations with a declining populace and uncover their singular tales. Delve into the annals of these lands, and be astounded by what you find! Uncover the mysteries of these countries, as you discover their remarkable stories!

In a crisis, people will turn to plants once again for both food and medicine.
And there are some plants that will vanish faster than all others.
So the only way to make sure you have them when you need them is to grow them in your own backyard.
P.S. However, there is a limited number of these seeds and the demand is huge–no wonder, with all that’s happening in the world right now. Click here to see if there are any left for you!
Venture into the untold chronicles of countries with dwindling populations. Unearth their remarkable accounts, from long ago to the present. Delve into the obstacles they have faced, accomplishments they have made, and secrets they keep. Investigate how these nations have advanced over time and what has led to their decrease in population. Uncover what initiatives are being taken to counteract this trend and how people and societies are adjusting to shifting conditions. Gain enlightenment on the past while gaining a greater appreciation of the current state of affairs.
.
Introduction

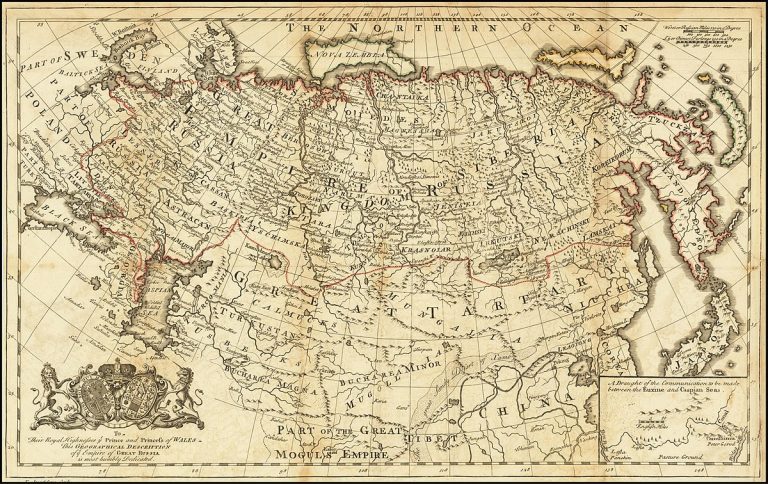
In recent times, a number of countries have experienced a perplexing phenomenon: population decline. Japan, Bulgaria, and Romania are among the most prominent examples of this trend, caused by a combination of factors such as low fertility rates, emigration, and aging populations.
Japan has seen its population decrease since 2008 due to an aging population and low birth rates, resulting in an economic downturn due to a shrinking workforce. To try to rectify this situation, the country has implemented policies to encourage immigration and boost fertility rates.
Bulgaria’s population has been on the decline since 1989 due to emigration and a low birth rate. The government has attempted to incentivize families with children through tax breaks but these measures have not had much success thus far.
Romania too has faced population decline since 1989 due to emigration and low fertility rates. The government has implemented various policies aimed at increasing the birth rate but these have yet to produce any significant impact in reversing the trend.
These countries demonstrate how neglecting demographic issues can lead to serious long-term consequences for economies and societies alike. It is therefore imperative that governments take steps to address such issues promptly in order to avoid further burstiness in their populations.
– Historical Causes of Negative Population Growth in Countries
Throughout the ages, population decline has been seen in countries everywhere, due to an array of causes. Whether from war and conflict, economic instability or environmental factors, the effects can be both deep and long-lasting.
In times of war, people may flee their homes in order to escape violence or destruction, leading to a decrease in the number of inhabitants. This is especially so during civil wars or international conflicts where whole communities are uprooted and displaced. In addition, high death tolls due to combat or disease can also bring about a significant drop in population size.
Economic instability can similarly result in negative population growth. When economies fail and resources become scarce, individuals may move elsewhere seeking better opportunities or more stable conditions. This could lead to a mass exodus from a certain country and thus fewer people living there over time. Governments can also impose strict regulations on birth rates or family sizes, further contributing to population decline as fewer children are born each year.
Lastly, environmental factors such as drought or famine may likewise cause negative population growth. If an area goes through extended periods of drought or famine that make it difficult for people to access food and water, they may migrate elsewhere searching for sustenance and better living conditions. Such migration could lead to decreased populations if enough people leave an area for extended periods of time.
– Examining the Long-Term Effects of Negative Population Trends
The ramifications of population decrease have been felt throughout the ages, with dire consequences for civilizations in days gone by. Take, for instance, the Roman Empire; its large-scale infrastructure was unable to be sustained due to a lack of citizens. In today’s world, countries facing diminishing populations struggle to support their economies and meet the needs of an aging population. To avoid further economic hardship, governments must take action to counteract these trends – offering incentives for families to increase their numbers, investing in education and healthcare programs that promote healthy living habits, and welcoming immigration are all steps that can be taken. With an understanding of how negative population trends have impacted history, we can better prepare ourselves for addressing them in our current era.
– Analyzing Historical Patterns of Migration and Depopulation
Examining the past can be a powerful way to perceive trends in migration and depopulation. By delving into the movements of people through time, we can gain insight into how individuals and communities have been impacted by changes in their environment, economic conditions, or political policies. Investigating historical patterns of migration and depopulation can provide invaluable information regarding how populations have shifted over time.
One approach to analyzing these patterns is to look at census data from different eras. Census records can offer comprehensive knowledge about population size, composition, and movement across time. This data can be used to discover trends in migratory flows and the consequences of various factors on population dispersal. For example, researchers may compare pre-industrial era population movements with those occurring during industrialization or urbanization periods to determine how certain elements could have affected the direction of migratory flows.
In addition, archival records such as letters, diaries, newspaper articles, travel reports, or personal accounts may be utilized to analyze historical patterns of migration and depopulation. These documents often contain detailed descriptions of people’s experiences as they moved from one place to another. Through these sources we can acquire a better comprehension of what motivated people to migrate or why certain areas experienced depopulation.
Qualitative research methods including interviews or focus groups are also useful for uncovering stories behind population movements that are not easily revealed through quantitative analysis alone. By conversing directly with individuals who have experienced migration or depopulation firsthand, researchers can gain valuable insights into the motivations behind these shifts in population dynamics.
By combining quantitative data analysis with qualitative research methods, researchers are able to comprehend the intricacies associated with historical patterns of migration and depopulation more thoroughly. Through this type of research we obtain a more extensive view into how populations shift over time and what factors contribute to these changes.
– Exploring the Impact of War on Negative Population Shifts
Time and again, war has proven to be a catalyst for population movements. Whether it’s the mass exodus of refugees from conflict-ridden countries or the internal displacement of citizens within their own borders, war can have a devastating effect on the populations of both aggressors and victims.
The most obvious consequence is the refugee crisis that ensues when people are forced to abandon their homes with nothing but the clothes on their backs. This mass migration can create a drastic decrease in population for both the country of origin and its neighboring countries, as well as an alteration in culture and economy due to influxes of new people seeking refuge.
On top of this, war can also lead to internal displacement within a nation’s borders caused by either violence or fear of persecution if one side wins over another. This could result in negative population shifts which could have far-reaching consequences for those affected.
Moreover, war has an indirect influence on population shifts through its economic implications. Conflict often leads to reduced economic activity due to destruction or disruption in trade routes and markets, resulting in poverty and famine that cause people to migrate out of affected areas in search of better opportunities elsewhere.
In summary, war has long been known for its destructive impact on populations around the world – creating negative population shifts with lasting effects on cultures, economies, and individuals alike.
– Investigating the Role of Economics in Declining Populations
The decline of many populations around the globe has been an issue that is heavily impacted by economics. From the Great Depression to the current economic recession, economics has had a major effect on population levels. During the Great Depression, unemployment rates skyrocketed, leading to decreased wages and less money for families to spend on food, housing, and other necessities. This caused people to leave their homes in search of better opportunities elsewhere or out of sheer desperation. Similarly, today’s economic recession has brought about high unemployment rates and financial hardship for many households, resulting in fewer births and more deaths due to poverty-related causes.
It is evident that economics can have a tremendous influence on population levels; however, it is essential to consider other factors as well. Political instability and wars can cause people to flee their homes or die from violence or disease. Environmental factors such as drought or flooding can lead to food shortages which result in malnutrition and death. Therefore, all facets of population decrease must be taken into account when investigating its causes.
To sum up, while economics plays an important part in population decline, it should not be viewed as the only factor responsible for this phenomenon. Other elements like politics, war, and environmental conditions must also be considered when studying population trends over time.
conclusion
Throughout the ages, certain nations have endured a decrease in their populace, be it through conflict, famine or other causes. Germany and Japan during World War II, Russia in its civil war of the early 1900s – these are but a few examples. Furthermore, some countries have experienced a reduction in population due to migratory movements or immigration regulations.
.
Some questions with answers
Q1. What countries have negative population?
A1. Currently, there are no countries with a negative population. However, some countries have seen their populations decline in the past.
Q2. What caused negative population in history?
A2. In history, negative population growth has been caused by war, famine, disease and emigration.
Q3. Has any country ever had a negative population?
A3. Yes, several countries have experienced periods of negative population growth in the past. For example, East Germany saw its population decline from 16 million to 12 million between 1989 and 1993.
Q4. What is the current trend for global population growth?
A4. The current trend for global population growth is positive and increasing at an accelerated rate due to improved healthcare and living standards in many parts of the world.
Q5. Are there any long-term effects of negative population growth?
A5. Yes, long-term effects of negative population growth can include economic stagnation or decline due to a lack of available workers and consumers as well as an aging population with fewer young people to support them financially through taxes and social programs.